
PPT CHAPTER 29 PRINCIPLES OF THE PowerPoint Presentation
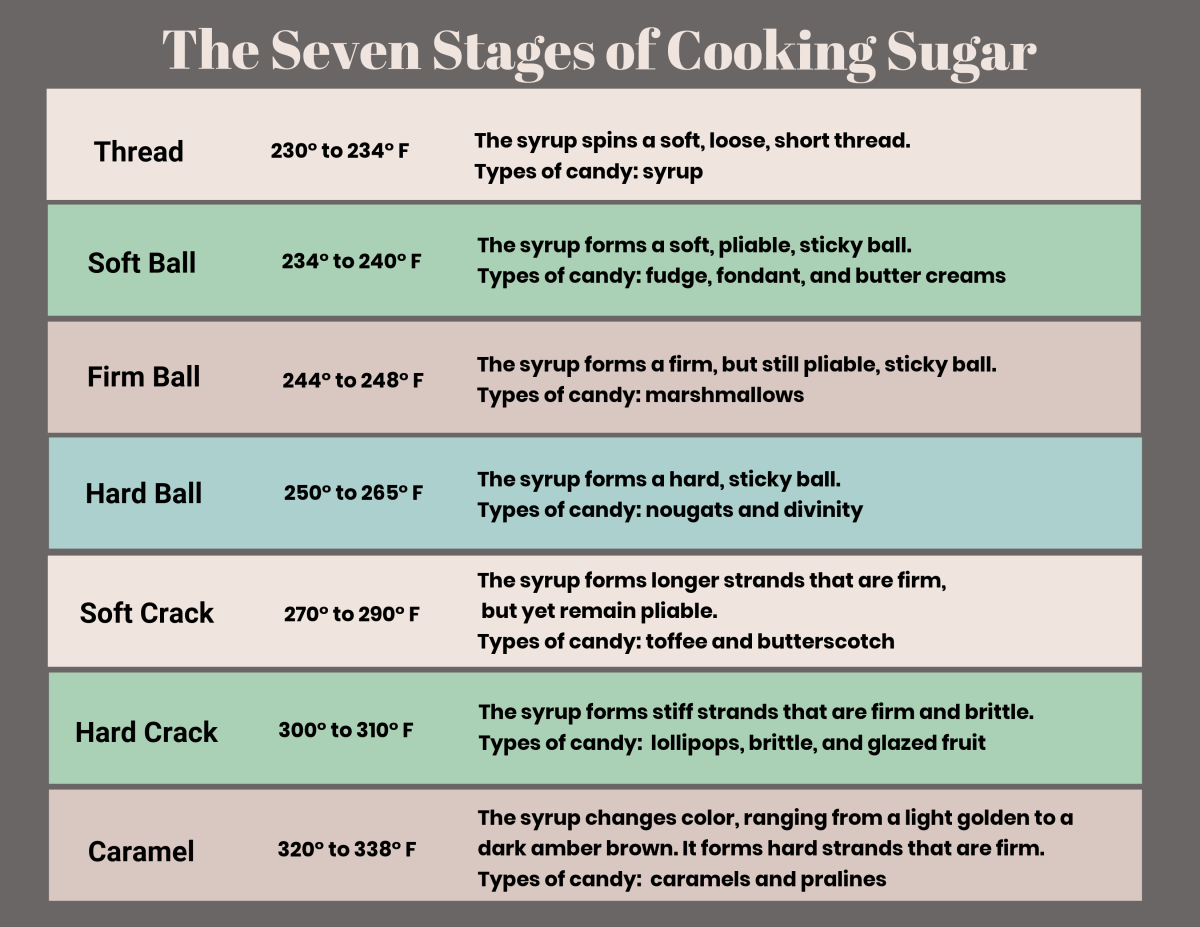
Sugar concentration; 80%. 223 °F - 235 °F. 106 °C - 112 °C. Syrups, Fruit pastes, Candied fruit. At this stage, the sugar syrup / candy syrup will still be clear. The syrup will form a fine "thread" or line when drizzled over ice water. The sugar at this temperature will still be liquid and will not set to make candy.

More Pumpkin! Pumpkin Salted Caramels Life Made Sweet Recipe Hard
Soft-Ball Stage: Soft-Ball Stage is a cooking term meaning that sugar syrup being heated has reached 112 - 116 C (234 - 240 F.) It is a test of how hot sugar syrup is, and of how much water is left in it. At this point of heating, the sugar concentration in the syrup is 85%. To test this stage a small amount of the sugar syrup could be

Stage of Sugar cooking YouTube
4. STAGES OF SUGAR COOKERY S. N O STAGES Fahrenhi et (F⁰) Celsius (C⁰) SUGAR CONCENTRATIO N APPERENCE USES 1. Thread 223-234 106-112 80% Syrup will form loose thread. Making sugar syrup 2. Soft ball 234-240 112-115 85% Form a soft, sticky ball can be flattened when removed from water. Caramels, butter creams 3.

Stages of Cooked Sugar Joy of cooking, Cooking and
Soft-Ball Stage. Soft-ball stage refers to a specific temperature range when cooking sugar syrups, occurring between 235 and 245 F. In addition to using a candy thermometer, this stage can be determined by dropping a spoonful of hot syrup into a bowl of very cold water. In the water, use your fingers to gather the cooled syrup into a ball.

STAGES OF SUGAR COOKERY Food chemistry lab Practical
The Wet Method is best. When making candy, place a 1- or 2-quart saucepan over medium-high heat until the pan is warm, not hot. Add the sugar and cook, stirring occasionally with a wooden spoon, until all of it has melted. Clamp on a Candy Thermometer.
The Science of Sugar Asia Society
Depending on the cooking time and temperature, sugar can transform into various stages, each resulting in different candy types. Let's explore the stages and their uses: Soft Ball Stage. The soft ball stage occurs when sugar syrup reaches a temperature of 235-240°F (113-116°C). At this stage, the sugar forms a soft ball when dropped into.

Stages of Sugar Cookery Demonstration YouTube
Take a spoon, and spoon out a bit. of the syrup and put into the ice bath. Do a few of them and see. Be sure not to touch the syrup. until you've cooled it in the ice water. It can burn you badly.

Sugar stages Wiki facts on this cookery method
Stages + Temperatures of Candy Making. 230° F-235° F - Thread Stage // sugar concentration: 80%. At this relatively low temperature, there is still a lot of water left in the syrup. When you drop a little of this syrup into cold water to cool, it forms a liquid thread that will not ball up. Cooking sugar syrup to this stage gives a thick.

Homemade Marshmallow Recipe Sugar Geek Show
Here are the primary stages of cooked sugar and what can be made at each point: Soft ball, 234° - 239°. Used for: mousseline buttercream, italian meringue, fondant, and fudge. Firm ball, 248° - 250°. Used for: caramel candy. Hard ball, 250° - 268°. At this point, the sugar is no longer malleable. Used for: marshmallows.
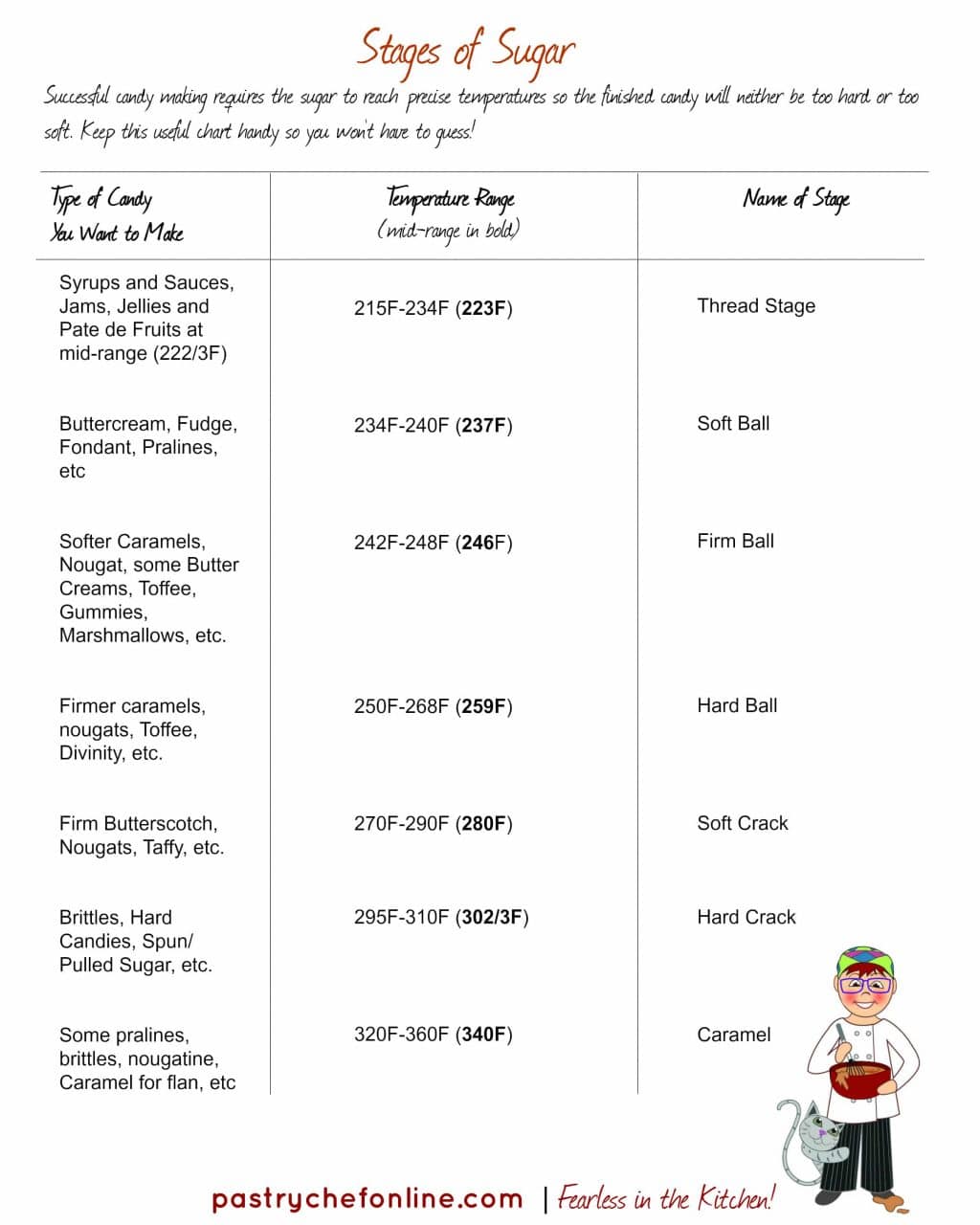
Stages of Sugar Chart Pastry Chef Online
Cooking of Sugar - various stages. There are 7 stages of cooking sugar. Thread: Cooked to 230° to 234°. The syrup spins a soft, loose, short thread. Soft Ball: Cooked to 234° to 240°. The syrup forms a soft, pliable, sticky ball. Firm Ball: Cooked to 244° to 248°. The syrup forms a firm, but still pliable, sticky ball.

STAGES OF SUGAR COOKERY Food chemistry lab Practical
Cooking sugar syrup to this stage gives you not candy, but syrup—something you might make to pour over ice cream. 1. Soft-Ball Stage 235° F-240° F sugar concentration: 85% At this temperature, sugar syrup dropped into cold water will form a soft, flexible ball. If you remove the ball from water, it will flatten like a pancake after a few.

Stages of Sugar Cookery
Hard Ball Stage. Temperature: 250° to 268°F. Description: The sugar will form a ball when it is dropped into the water, and it will be very firm and keep its shape well when pressed. However, it will feel sticky. You will have to press very hard to get it to change shape. Candy Types: Nougat, marshmallows, rock candy.
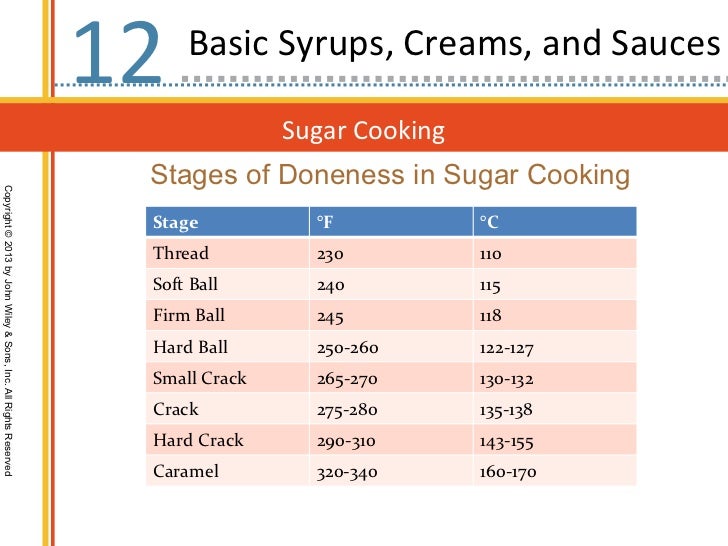
Ch12 basic syrups, creams, and sauces
Published on November 6, 2007. The primary step in candy making is to boil water (and, sometimes, other ingredients, such as butter, corn syrup, or milk, depending on the candy being made) and.

Does caramelising sugar affect speed of fermentation and final flavour
295 - 310. 146 - 155. Syrup will form threads that are stiff (brittle) and break easily. Used for brittles, toffees, glazed fruit, hard candy, pulled poured and spun sugar. Caramel. 320 - 360. 160 - 182. Syrup will become transparent and will change color, ranging from light golden brown to dark amber.

STAGES OF SUGAR COOKERY Food chemistry lab Practical
The structure of the final sugar also changes as the sugar cooks. Cook briefly and you'll get a simple sugar syrup. Cooked a little more and you'll get a gooey, sticky sap. Cooked until almost all the molecules have recombined and you'll end up with a hard, brittle candy. At any point in this process, we can stop the cooking and have a.

Cooking of Sugar various stages hmhub
270-290 degrees F. 132-143 degrees C. Syrup will form strands that are firm yet pliable. Used for butterscotch, firm nougat, and taffy. Hard Crack. 295-310 degrees F. 146-155 degrees C. Syrup will form threads that are stiff (brittle) and break easily. Used for brittles, toffees, glazed fruit, hard candy, pulled poured and spun sugar.